Which Chart Type Displays The Data Horizontally
When yous create a chart in an Excel worksheet, a Word certificate, or a PowerPoint presentation, yous have a lot of options. Whether you'll use a chart that's recommended for your data, 1 that y'all'll pick from the list of all charts, or one from our selection of nautical chart templates, it might help to know a picayune more about each type of nautical chart.
Click here to first creating a chart.
For a description of each nautical chart type, select an pick from the following drib-down list.
Data that's arranged in columns or rows on a worksheet can be plotted in a column chart. A cavalcade chart typically displays categories along the horizontal (category) axis and values forth the vertical (value) axis, as shown in this chart:
Types of cavalcade charts
-
Amassed cavalcade and 3-D clustered column

A clustered cavalcade chart shows values in 2-D columns. A 3-D clustered cavalcade chart shows columns in 3-D format, but information technology doesn't use a third value centrality (depth axis). Apply this chart when you accept categories that correspond:
-
Ranges of values (for example, item counts).
-
Specific scale arrangements (for example, a Likert scale with entries like Strongly agree, Agree, Neutral, Disagree, Strongly disagree).
-
Names that are non in whatsoever specific order (for example, item names, geographic names, or the names of people).
-
-
Stacked column and 3-D stacked column A stacked column chart shows values in two-D stacked columns. A 3-D stacked column chart shows the stacked columns in 3-D format, but it doesn't apply a depth axis. Use this chart when you have multiple data series and yous want to emphasize the total.

-
100% stacked column and 3-D 100% stacked column A 100% stacked column nautical chart shows values in 2-D columns that are stacked to represent 100%. A 3-D 100% stacked column chart shows the columns in 3-D format, but it doesn't utilize a depth axis. Use this nautical chart when yous have two or more data series and you desire to emphasize the contributions to the whole, particularly if the full is the same for each category.

-
iii-D column 3-D column charts use three axes that you can alter (a horizontal centrality, a vertical axis, and a depth axis), and they compare data points along the horizontal and the depth axes. Use this chart when yous want to compare data across both categories and data series.

Data that'south arranged in columns or rows on a worksheet can exist plotted in a line chart. In a line chart, category data is distributed evenly along the horizontal axis, and all value data is distributed evenly along the vertical centrality. Line charts can show continuous information over time on an evenly scaled centrality, so they're ideal for showing trends in information at equal intervals, like months, quarters, or fiscal years.
Types of line charts
-
Line and line with markers Shown with or without markers to bespeak private data values, line charts tin show trends over time or evenly spaced categories, especially when you take many information points and the social club in which they are presented is of import. If there are many categories or the values are approximate, apply a line nautical chart without markers.

-
Stacked line and stacked line with markers Shown with or without markers to indicate private information values, stacked line charts can testify the trend of the contribution of each value over time or evenly spaced categories.

-
100% stacked line and 100% stacked line with markers Shown with or without markers to indicate individual data values, 100% stacked line charts tin show the trend of the percentage each value contributes over time or evenly spaced categories. If there are many categories or the values are judge, utilize a 100% stacked line nautical chart without markers.
-
3-D line 3-D line charts show each row or column of data as a 3-D ribbon. A three-D line chart has horizontal, vertical, and depth axes that you can change.
Notes:
-
Line charts piece of work best when you take multiple data serial in your chart—if you have only one data series, consider using a scatter chart instead.
-
Stacked line charts sum the data, which might not exist the result yous want. It might not exist easy to see that the lines are stacked, so consider using a different line chart type or a stacked surface area chart instead.
-
Data that's bundled in one column or row on a worksheet can be plotted in a pie chart. Pie charts show the size of items in one information series, proportional to the sum of the items. The data points in a pie chart are shown every bit a pct of the whole pie.
Consider using a pie chart when:
-
You take only i data serial.
-
None of the values in your data are negative.
-
Almost none of the values in your data are zero values.
-
You take no more than vii categories, all of which represent parts of the whole pie.
Types of pie charts
-
Pie and 3-D pie Pie charts prove the contribution of each value to a full in a two-D or 3-D format. You tin pull out slices of a pie chart manually to emphasize the slices.

-
Pie of pie and bar of pie Pie of pie or bar of pie charts show pie charts with smaller values pulled out into a secondary pie or stacked bar nautical chart, which makes them easier to distinguish.

Data that's bundled in columns or rows only on a worksheet can be plotted in a doughnut chart. Like a pie chart, a doughnut chart shows the human relationship of parts to a whole, but it can comprise more than i information series.
Types of doughnut charts
-
Doughnut Doughnut charts show data in rings, where each band represents a data series. If percentages are shown in information labels, each ring will full 100%.

Note:Doughnut charts aren't easy to read. Y'all may want to use a stacked cavalcade charts or Stacked bar chart instead.
Data that's arranged in columns or rows on a worksheet can be plotted in a bar chart. Bar charts illustrate comparisons among individual items. In a bar nautical chart, the categories are typically organized along the vertical axis, and the values along the horizontal axis.
Consider using a bar chart when:
-
The axis labels are long.
-
The values that are shown are durations.
Types of bar charts
-
Clustered bar and three-D clustered bar A clustered bar chart shows bars in 2-D format. A three-D amassed bar nautical chart shows bars in three-D format; information technology doesn't use a depth axis.

-
Stacked bar and iii-D stacked bar Stacked bar charts show the human relationship of individual items to the whole in 2-D confined. A 3-D stacked bar chart shows bars in 3-D format; it doesn't apply a depth axis.

-
100% stacked bar and three-D 100% stacked bar A 100% stacked bar shows 2-D bars that compare the percentage that each value contributes to a total across categories. A 3-D 100% stacked bar chart shows confined in 3-D format; information technology doesn't use a depth centrality.

Data that's bundled in columns or rows on a worksheet can be plotted in an area chart. Expanse charts can be used to plot change over time and depict attention to the total value across a trend. By showing the sum of the plotted values, an area nautical chart also shows the relationship of parts to a whole.
Types of area charts
-
Area and 3-D area Shown in two-D or in iii-D format, area charts show the trend of values over time or other category data. 3-D expanse charts use three axes (horizontal, vertical, and depth) that you tin change. As a rule, consider using a line chart instead of a non-stacked expanse chart, considering data from one series can exist hidden backside data from another series.

-
Stacked area and three-D stacked area Stacked area charts show the tendency of the contribution of each value over time or other category data in 2-D format. A 3-D stacked surface area chart does the same, but it shows areas in 3-D format without using a depth axis.

-
100% stacked expanse and iii-D 100% stacked area 100% stacked surface area charts show the trend of the pct that each value contributes over time or other category information. A iii-D 100% stacked surface area chart does the aforementioned, but it shows areas in three-D format without using a depth axis.

Information that'south arranged in columns and rows on a worksheet can exist plotted in an xy (scatter) nautical chart. Place the x values in one row or column, and so enter the corresponding y values in the adjacent rows or columns.
A besprinkle chart has two value axes: a horizontal (ten) and a vertical (y) value centrality. It combines x and y values into single data points and shows them in irregular intervals, or clusters. Scatter charts are typically used for showing and comparing numeric values, similar scientific, statistical, and engineering information.
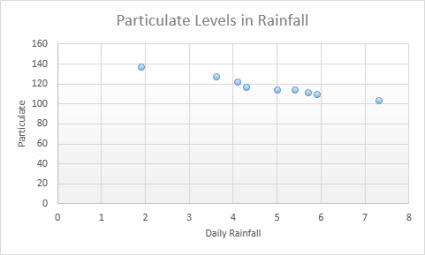
Consider using a scatter chart when:
-
You want to modify the scale of the horizontal centrality.
-
You want to brand that axis a logarithmic scale.
-
Values for horizontal axis are not evenly spaced.
-
At that place are many data points on the horizontal axis.
-
You desire to adjust the independent axis scales of a scatter nautical chart to reveal more than information most data that includes pairs or grouped sets of values.
-
Y'all want to show similarities between large sets of data instead of differences between information points.
-
You want to compare many information points without regard to time—the more than data that you include in a scatter nautical chart, the meliorate the comparisons y'all can make.
Types of scatter charts
-
Scatter This chart shows data points without connecting lines to compare pairs of values.
-
Scatter with smooth lines and markers and scatter with smooth lines This chart shows a smooth curve that connects the data points. Smooth lines can be shown with or without markers. Use a smoothen line without markers if there are many data points.

-
Besprinkle with straight lines and markers and scatter with straight lines This chart shows directly connecting lines between data points. Straight lines can be shown with or without markers.

Much like a besprinkle chart, a bubble chart adds a third cavalcade to specify the size of the bubbling information technology shows to represent the information points in the data series.
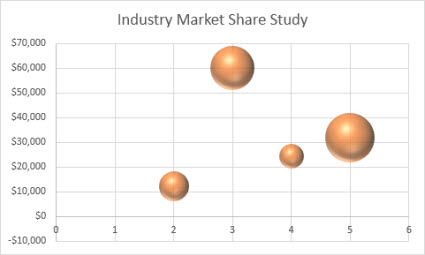
Blazon of bubble charts
-
Chimera or chimera with 3-D consequence Both of these bubble charts compare sets of three values instead of 2, showing bubbles in 2-D or 3-D format (without using a depth centrality). The third value specifies the size of the bubble marker.

Data that's arranged in columns or rows in a specific order on a worksheet tin exist plotted in a stock chart. As the name implies, stock charts can testify fluctuations in stock prices. Notwithstanding, this chart can also show fluctuations in other data, similar daily rainfall or annual temperatures. Make sure you lot organize your data in the correct order to create a stock chart.
For case, to create a simple high-low-shut stock chart, adapt your data with High, Low, and Close entered as column headings, in that order.
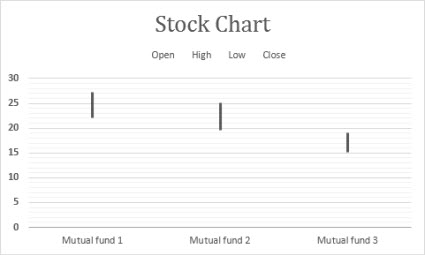
Types of stock charts
-
High-low-close This stock chart uses iii series of values in the following order: high, depression, and then close.
-
Open-high-low-close This stock chart uses four series of values in the following order: open, high, low, and then close.
-
Volume-high-low-shut This stock chart uses iv serial of values in the following order: volume, high, depression, and and then close. Information technology measures volume by using two value axes: i for the columns that measure volume, and the other for the stock prices.
-
Book-open-high-low-close This stock chart uses 5 series of values in the following order: volume, open up, high, low, and so close.

Data that's arranged in columns or rows on a worksheet can exist plotted in a surface chart. This chart is useful when you want to find optimum combinations between two sets of information. As in a topographic map, colors and patterns indicate areas that are in the aforementioned range of values. Y'all tin can create a surface chart when both categories and data serial are numeric values.
Types of surface charts
-
3-D surface This chart shows a 3-D view of the information, which can be imagined as a rubber sail stretched over a iii-D cavalcade nautical chart. It is typically used to prove relationships between large amounts of data that may otherwise be difficult to see. Color bands in a surface chart exercise not represent the data series; they indicate the difference between the values.
-
Wireframe 3-D surface Shown without color on the surface, a three-D surface nautical chart is called a wireframe iii-D surface chart. This chart shows only the lines. A wireframe 3-D surface chart isn't easy to read, but information technology can plot large data sets much faster than a 3-D surface nautical chart.

-
Contour Contour charts are surface charts viewed from above, similar to ii-D topographic maps. In a profile chart, color bands represent specific ranges of values. The lines in a contour chart connect interpolated points of equal value.

-
Wireframe contour Wireframe contour charts are besides surface charts viewed from above. Without colour bands on the surface, a wireframe nautical chart shows only the lines. Wireframe contour charts aren't easy to read. You may desire to employ a three-D surface chart instead.
Data that's bundled in columns or rows on a worksheet can be plotted in a radar chart. Radar charts compare the aggregate values of several data series.
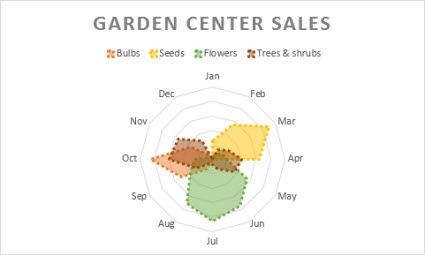
Type of radar charts
-
Radar and radar with markers With or without markers for individual data points, radar charts show changes in values relative to a heart point.

-
Filled radar In a filled radar nautical chart, the surface area covered by a information series is filled with a color.

The treemap chart provides a hierarchical view of your data and an easy way to compare different levels of categorization. The treemap chart displays categories by color and proximity and can easily show lots of data which would be hard with other chart types. The treemap chart tin be plotted when empty (blank) cells be inside the hierarchal construction and treemap charts are practiced for comparing proportions within the hierarchy.
Note:There are no chart sub-types for treemap charts.
The sunburst chart is ideal for displaying hierarchical data and can exist plotted when empty (bare) cells exist within the hierarchal structure . Each level of the hierarchy is represented by one ring or circle with the innermost circle as the elevation of the hierarchy. A sunburst nautical chart without any hierarchical data (one level of categories), looks similar to a doughnut chart. Nonetheless, a sunburst nautical chart with multiple levels of categories shows how the outer rings chronicle to the inner rings. The sunburst nautical chart is well-nigh effective at showing how one ring is cleaved into its contributing pieces.
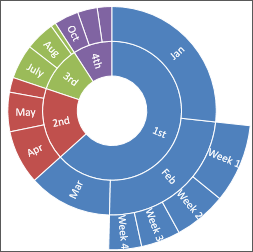
Note:At that place are no nautical chart sub-types for sunburst charts.
Information plotted in a histogram nautical chart shows the frequencies within a distribution. Each column of the chart is called a bin, which tin can be changed to further analyze your data.
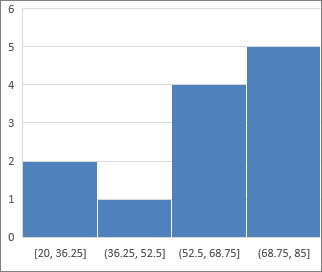
Blazon of histogram charts
-
Histogram The histogram chart shows the distribution of your data grouped into frequency bins.

-
Pareto nautical chart A pareto is a sorted histogram chart that contains both columns sorted in descending guild and a line representing the cumulative full percent.

A box and whisker chart shows distribution of information into quartiles, highlighting the mean and outliers. The boxes may accept lines extending vertically called "whiskers". These lines bespeak variability outside the upper and lower quartiles, and any point exterior those lines or whiskers is considered an outlier. Utilize this chart type when in that location are multiple data sets which chronicle to each other in some way.
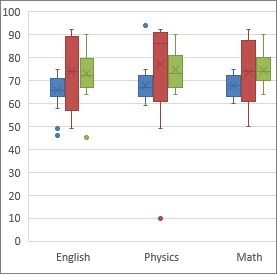
Note:At that place are no chart sub-types for box and whisker charts.
A waterfall chart shows a running full of your financial data as values are added or subtracted. It's useful for agreement how an initial value is afflicted by a serial of positive and negative values. The columns are color coded so y'all can speedily tell positive from negative numbers.
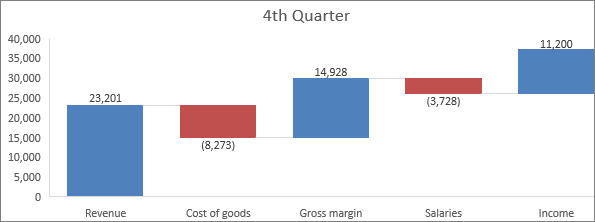
Note:In that location are no chart sub-types for waterfall charts.
Funnel charts show values across multiple stages in a procedure.

Typically, the values decrease gradually, allowing the bars to resemble a funnel. Read more about funnel charts hither.
Information that's arranged in columns and rows tin can be plotted in a combo nautical chart. Combo charts combine two or more chart types to make the data easy to understand, especially when the data is widely varied. Shown with a secondary axis, this chart is fifty-fifty easier to read. In this case, we used a cavalcade chart to show the number of homes sold between January and June and and then used a line chart to arrive easier for readers to quickly identify the average sales price by month.
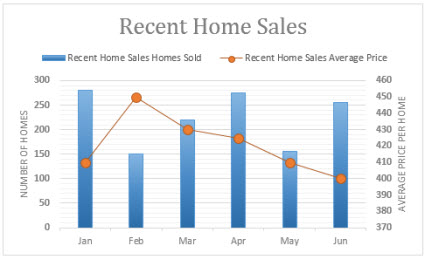
Type of combo charts
-
Amassed column – line and clustered column – line on secondary centrality With or without a secondary centrality, this chart combines a clustered column and line chart, showing some data series as columns and others as lines in the same chart.

-
Stacked area – clustered cavalcade This chart combines a stacked area and clustered column chart, showing some data series as stacked areas and others as columns in the same chart.

-
Custom combination This chart lets you combine the charts you want to show in the aforementioned chart.

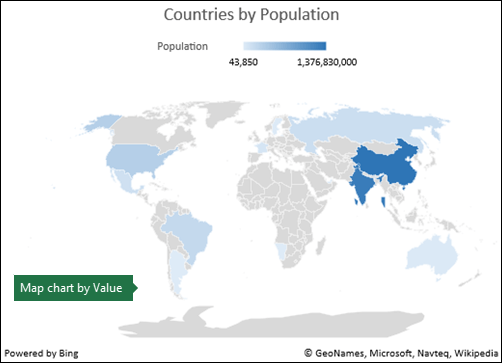
You can utilise a Map Nautical chart to compare values and bear witness categories beyond geographical regions. Use information technology when you have geographical regions in your data, like countries/regions, states, counties or postal codes.
For case, Countries past Population uses values. The values represent the total population in each land, with each portrayed using a gradient spectrum of 2 colors. The color for each region is dictated by where along the spectrum its value falls with respect to the others.
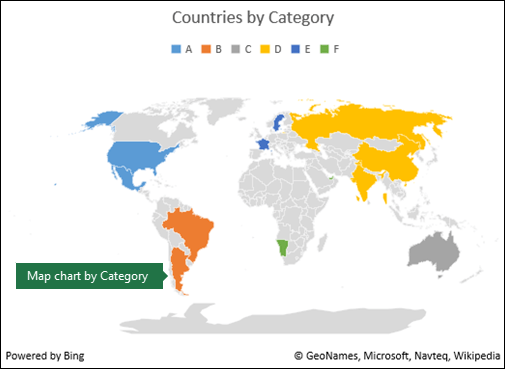
In the post-obit instance, Countries past Category, the categories are displayed using a standard legend to show groups or affiliations. Each data point is represented past an entirely different colour.
Change a nautical chart type
If you have already have a chart, just you just want to change its type:
-
Select the nautical chart, click the Blueprint tab, and click Change Chart Blazon.

-
Choose a new chart type in the Modify Nautical chart Type box.
Many nautical chart types are available to help you brandish data in means that are meaningful to your audience. Hither are some examples of the virtually common chart types and how they can be used.
Data that is arranged in columns or rows on an Excel sheet can be plotted in a column chart. In cavalcade charts, categories are typically organized forth the horizontal axis and values along the vertical axis.
Column charts are useful to show how data changes over time or to show comparisons among items.
Column charts have the following chart subtypes:
-
Clustered column chart Compares values across categories. A clustered cavalcade chart displays values in two-D vertical rectangles. A clustered cavalcade in a 3-D nautical chart displays the data by using a iii-D perspective.
-
Stacked cavalcade nautical chart Shows the human relationship of individual items to the whole, comparison the contribution of each value to a total across categories. A stacked column chart displays values in 2-D vertical stacked rectangles. A three-D stacked column nautical chart displays the data by using a 3-D perspective. A three-D perspective is non a truthful 3-D nautical chart because a third value axis (depth axis) is not used.
-
100% stacked column chart Compares the percent that each value contributes to a total beyond categories. A 100% stacked column chart displays values in ii-D vertical 100% stacked rectangles. A 3-D 100% stacked column chart displays the data by using a three-D perspective. A 3-D perspective is not a true iii-D chart considering a tertiary value axis (depth axis) is non used.
-
iii-D column chart Uses three axes that you can change (a horizontal axis, a vertical axis, and a depth axis). They compare information points forth the horizontal and the depth axes.
Information that is arranged in columns or rows on an Excel sheet can be plotted in a line nautical chart. Line charts can display continuous information over time, fix confronting a common scale, and are therefore ideal to testify trends in information at equal intervals. In a line chart, category data is distributed evenly forth the horizontal axis, and all value data is distributed evenly along the vertical centrality.
Line charts work well if your category labels are text, and represent evenly spaced values such every bit months, quarters, or fiscal years.
Line charts accept the following nautical chart subtypes:
-
Line chart with or without markers Shows trends over time or ordered categories, particularly when at that place are many data points and the order in which they are presented is important. If there are many categories or the values are approximate, employ a line chart without markers.
-
Stacked line chart with or without markers Shows the trend of the contribution of each value over fourth dimension or ordered categories. If there are many categories or the values are approximate, use a stacked line chart without markers.
-
100% stacked line chart displayed with or without markers Shows the trend of the percentage each value contributes over time or ordered categories. If there are many categories or the values are estimate, use a 100% stacked line chart without markers.
-
3-D line chart Shows each row or column of data as a 3-D ribbon. A 3-D line nautical chart has horizontal, vertical, and depth axes that you can change.
Data that is arranged in 1 column or row only on an Excel sheet can be plotted in a pie nautical chart. Pie charts bear witness the size of items in i data series, proportional to the sum of the items. The information points in a pie chart are displayed every bit a percentage of the whole pie.
Consider using a pie chart when y'all have just 1 data series that yous want to plot, none of the values that you want to plot are negative, almost none of the values that you want to plot are null values, you lot don't have more than seven categories, and the categories correspond parts of the whole pie.
Pie charts take the post-obit chart subtypes:
-
Pie chart Displays the contribution of each value to a total in a ii-D or three-D format. You can pull out slices of a pie nautical chart manually to emphasize the slices.
-
Pie of pie or bar of pie chart Displays pie charts with user-divers values that are extracted from the main pie nautical chart and combined into a secondary pie chart or into a stacked bar chart. These chart types are useful when yous want to make small slices in the main pie chart easier to distinguish.
-
Doughnut chart Like a pie chart, a doughnut chart shows the human relationship of parts to a whole. Even so, it can contain more than than one information series. Each band of the doughnut chart represents a information series. Displays data in rings, where each ring represents a data series. If percentages are displayed in data labels, each band will total 100%.
Data that is arranged in columns or rows on an Excel canvass can be plotted in a bar chart.
Use bar charts to bear witness comparisons among private items.
Bar charts have the following chart subtypes:
-
Clustered bar and 3-D Amassed bar chart Compares values across categories. In a amassed bar chart, the categories are typically organized along the vertical centrality, and the values along the horizontal axis. A clustered bar in iii-D nautical chart displays the horizontal rectangles in 3-D format. Information technology does not display the data on 3 axes.
-
Stacked bar and three-D Stacked bar chart Shows the human relationship of individual items to the whole. A stacked bar in 3-D chart displays the horizontal rectangles in 3-D format. It does non display the data on three axes.
-
100% stacked bar chart and 100% stacked bar chart in 3-D Compares the percent that each value contributes to a total across categories. A 100% stacked bar in 3-D nautical chart displays the horizontal rectangles in 3-D format. It does not brandish the information on three axes.
Data that is arranged in columns and rows on an Excel sheet can be plotted in an xy (scatter) chart. A scatter nautical chart has two value axes. It shows one set of numeric information along the horizontal axis (x-axis) and another forth the vertical axis (y-axis). Information technology combines these values into single data points and displays them in irregular intervals, or clusters.
Besprinkle charts show the relationships among the numeric values in several data series, or plot two groups of numbers equally one serial of xy coordinates. Scatter charts are typically used for displaying and comparing numeric values, such equally scientific, statistical, and applied science data.
Scatter charts take the following nautical chart subtypes:
-
Scatter chart Compares pairs of values. Employ a scatter nautical chart with data markers but without lines if you take many data points and connecting lines would brand the data more difficult to read. Y'all can also utilise this chart type when you exercise not accept to testify connectivity of the data points.
-
Scatter chart with smooth lines and besprinkle chart with smooth lines and markers Displays a smooth curve that connects the data points. Smooth lines can be displayed with or without markers. Use a smoothen line without markers if there are many data points.
-
Besprinkle nautical chart with straight lines and scatter chart with straight lines and markers Displays direct connecting lines between information points. Straight lines can be displayed with or without markers.
-
Bubble nautical chart or bubble chart with three-D result A bubble chart is a kind of xy (scatter) nautical chart, where the size of the bubble represents the value of a 3rd variable. Compares sets of three values instead of two. The tertiary value determines the size of the bubble marker. Y'all can cull to display bubbling in ii-D format or with a 3-D effect.
Data that is arranged in columns or rows on an Excel sheet can exist plotted in an area chart. By displaying the sum of the plotted values, an area chart also shows the relationship of parts to a whole.
Expanse charts emphasize the magnitude of change over time, and tin be used to draw attention to the total value across a trend. For example, data that represents profit over time can exist plotted in an area nautical chart to emphasize the total profit.
Area charts take the post-obit chart subtypes:
-
Area chart Displays the trend of values over time or other category data. three-D expanse charts utilise iii axes (horizontal, vertical, and depth) that you lot tin change. More often than not, consider using a line chart instead of a nonstacked expanse chart considering data from ane series can exist obscured by information from another series.
-
Stacked area chart Displays the tendency of the contribution of each value over time or other category information. A stacked area chart in three-D is displayed in the aforementioned manner simply uses a 3-D perspective. A 3-D perspective is not a truthful 3-D nautical chart because a third value centrality (depth axis) is not used.
-
100% stacked area nautical chart Displays the trend of the percentage that each value contributes over fourth dimension or other category data. A 100% stacked area nautical chart in three-D is displayed in the same style but uses a three-D perspective. A 3-D perspective is not a true 3-D nautical chart because a third value axis (depth axis) is not used.
Data that is arranged in columns or rows in a specific order on an Excel sail can be plotted in a stock nautical chart.
As its name implies, a stock chart is most frequently used to testify the fluctuation of stock prices. Still, this chart may also be used for scientific data. For instance, yous could use a stock chart to indicate the fluctuation of daily or annual temperatures.
Stock charts take the following chart sub-types:
-
High-Low-Close stock chart Illustrates stock prices. It requires iii serial of values in the right gild: high, low, and so close.
-
Open-High-Low-Close stock chart Requires four serial of values in the correct order: open, high, depression, and and then close.
-
Volume-High-Low-Close stock nautical chart Requires four series of values in the correct order: volume, high, low, and then shut. Information technology measures book by using two value axes: one for the columns that mensurate book, and the other for the stock prices.
-
Book-Open-Loftier-Low-Shut stock nautical chart Requires five series of values in the correct lodge: volume, open, high, low, and then shut.
Information that is arranged in columns or rows on an Excel canvas can be plotted in a surface chart. As in a topographic map, colors and patterns indicate areas that are in the same range of values.
A surface chart is useful when you desire to find optimal combinations betwixt 2 sets of data.
Surface charts have the following chart subtypes:
-
3-D surface nautical chart Shows trends in values across ii dimensions in a continuous curve. Color bands in a surface chart exercise not represent the data series. They stand for the departure between the values. This nautical chart shows a 3-D view of the data, which tin can be imagined as a condom sheet stretched over a 3-D column chart. Information technology is typically used to show relationships betwixt big amounts of data that may otherwise be difficult to see.
-
Wireframe 3-D surface chart Shows simply the lines. A wireframe 3-D surface chart is not piece of cake to read, but this chart type is useful for faster plotting of large data sets.
-
Contour chart Surface charts viewed from above, similar to 2-D topographic maps. In a contour nautical chart, colour bands represent specific ranges of values. The lines in a profile nautical chart connect interpolated points of equal value.
-
Wireframe profile chart Surface charts viewed from to a higher place. Without color bands on the surface, a wireframe chart shows but the lines. Wireframe contour charts are not like shooting fish in a barrel to read. Y'all may want to use a three-D surface chart instead.
In a radar chart, each category has its own value axis radiating from the center point. Lines connect all the values in the same series.
Employ radar charts to compare the aggregate values of several data serial.
Radar charts have the following nautical chart subtypes:
-
Radar chart Displays changes in values in relation to a center point.
-
Radar with markers Displays changes in values in relation to a center point with markers.
-
Filled radar nautical chart Displays changes in values in relation to a center point, and fills the area covered by a data series with color.
You tin can employ a Map Chart to compare values and show categories across geographical regions. Use it when yous take geographical regions in your data, similar countries/regions, states, counties or postal codes.
For more information, run across Create a map chart.
Funnel charts show values across multiple stages in a procedure.

Typically, the values decrease gradually, allowing the bars to resemble a funnel. For more information, see Create a funnel chart.
The treemap chart provides a hierarchical view of your data and an easy way to compare dissimilar levels of categorization. The treemap chart displays categories by color and proximity and tin can easily testify lots of data which would be difficult with other chart types. The treemap chart can be plotted when empty (blank) cells exist within the hierarchal construction and treemap charts are skillful for comparison proportions within the hierarchy.

At that place are no chart sub-types for treemap charts.
For more data, come across Create a treemap chart.
The sunburst chart is ideal for displaying hierarchical data and can be plotted when empty (bare) cells exist within the hierarchal construction . Each level of the hierarchy is represented by one ring or circle with the innermost circle as the height of the hierarchy. A sunburst chart without whatever hierarchical data (ane level of categories), looks similar to a doughnut nautical chart. However, a sunburst chart with multiple levels of categories shows how the outer rings relate to the inner rings. The sunburst chart is most effective at showing how one ring is cleaved into its contributing pieces.

In that location are no chart sub-types for sunburst charts.
For more information, encounter Create a sunburst chart.
A waterfall chart shows a running full of your financial data every bit values are added or subtracted. Information technology's useful for understanding how an initial value is affected past a series of positive and negative values. The columns are color coded and then you can quickly tell positive from negative numbers.

There are no nautical chart sub-types for waterfall charts.
For more information, see Create a waterfall nautical chart.
Data plotted in a histogram chart shows the frequencies within a distribution. Each column of the nautical chart is called a bin, which can exist inverse to further analyze your information.

Types of histogram charts
-
Histogram The histogram nautical chart shows the distribution of your data grouped into frequency bins.

-
Pareto nautical chart A pareto is a sorted histogram chart that contains both columns sorted in descending order and a line representing the cumulative full percentage.

More than data is available for Histogram and Pareto charts.
A box and whisker chart shows distribution of data into quartiles, highlighting the mean and outliers. The boxes may take lines extending vertically called "whiskers". These lines indicate variability exterior the upper and lower quartiles, and any point outside those lines or whiskers is considered an outlier. Use this chart blazon when there are multiple data sets which chronicle to each other in some way.

For more data, see Create a box and whisker chart.

Information that is arranged in columns or rows on an Excel canvass can be plotted in a column nautical chart. In column charts, categories are typically organized forth the horizontal centrality and values along the vertical axis.
Column charts are useful to show how data changes over time or to show comparisons among items.
Cavalcade charts have the following chart subtypes:
-
Clustered column chart Compares values across categories. A clustered column chart displays values in 2-D vertical rectangles. A amassed cavalcade in a 3-D nautical chart displays the data by using a iii-D perspective.
-
Stacked column chart Shows the relationship of private items to the whole, comparison the contribution of each value to a total across categories. A stacked column chart displays values in 2-D vertical stacked rectangles. A 3-D stacked column nautical chart displays the data by using a three-D perspective. A iii-D perspective is not a truthful three-D chart because a third value axis (depth axis) is not used.
-
100% stacked cavalcade nautical chart Compares the per centum that each value contributes to a total across categories. A 100% stacked column nautical chart displays values in ii-D vertical 100% stacked rectangles. A 3-D 100% stacked column chart displays the data past using a three-D perspective. A 3-D perspective is not a true 3-D nautical chart because a third value axis (depth axis) is not used.
-
3-D column chart Uses three axes that yous can alter (a horizontal axis, a vertical axis, and a depth axis). They compare data points along the horizontal and the depth axes.
-
Cylinder, cone, and pyramid nautical chart Available in the same clustered, stacked, 100% stacked, and three-D chart types that are provided for rectangular cavalcade charts. They show and compare information in the same manner. The but difference is that these chart types brandish cylinder, cone, and pyramid shapes instead of rectangles.

Data that is bundled in columns or rows on an Excel sheet tin exist plotted in a line chart. Line charts can display continuous data over time, fix against a common calibration, and are therefore ideal to testify trends in data at equal intervals. In a line chart, category data is distributed evenly along the horizontal centrality, and all value data is distributed evenly along the vertical axis.
Line charts work well if your category labels are text, and represent evenly spaced values such as months, quarters, or fiscal years.
Line charts have the following chart subtypes:
-
Line chart with or without markers Shows trends over time or ordered categories, especially when there are many data points and the society in which they are presented is important. If at that place are many categories or the values are guess, use a line chart without markers.
-
Stacked line chart with or without markers Shows the trend of the contribution of each value over time or ordered categories. If there are many categories or the values are approximate, utilise a stacked line chart without markers.
-
100% stacked line nautical chart displayed with or without markers Shows the trend of the percentage each value contributes over fourth dimension or ordered categories. If at that place are many categories or the values are approximate, use a 100% stacked line chart without markers.
-
3-D line chart Shows each row or column of data as a iii-D ribbon. A iii-D line nautical chart has horizontal, vertical, and depth axes that y'all can alter.

Data that is bundled in 1 column or row only on an Excel sheet tin can exist plotted in a pie chart. Pie charts show the size of items in i information series, proportional to the sum of the items. The data points in a pie chart are displayed as a pct of the whole pie.
Consider using a pie nautical chart when you take but ane data series that you want to plot, none of the values that you lot desire to plot are negative, well-nigh none of the values that you desire to plot are zero values, you lot don't take more than than vii categories, and the categories represent parts of the whole pie.
Pie charts have the following chart subtypes:
-
Pie chart Displays the contribution of each value to a full in a ii-D or three-D format. You tin can pull out slices of a pie nautical chart manually to emphasize the slices.
-
Pie of pie or bar of pie chart Displays pie charts with user-defined values that are extracted from the main pie nautical chart and combined into a secondary pie chart or into a stacked bar nautical chart. These chart types are useful when you want to brand small slices in the primary pie chart easier to distinguish.
-
Exploded pie nautical chart Displays the contribution of each value to a total while emphasizing individual values. Exploded pie charts can be displayed in iii-D format. Y'all can change the pie explosion setting for all slices and individual slices. However, you cannot move the slices of an exploded pie manually.

Data that is bundled in columns or rows on an Excel sheet tin can be plotted in a bar chart.
Apply bar charts to testify comparisons amongst individual items.
Bar charts have the following chart subtypes:
-
Clustered bar chart Compares values across categories. In a clustered bar chart, the categories are typically organized along the vertical axis, and the values along the horizontal centrality. A clustered bar in 3-D nautical chart displays the horizontal rectangles in iii-D format. It does not display the data on 3 axes.
-
Stacked bar chart Shows the human relationship of individual items to the whole. A stacked bar in 3-D chart displays the horizontal rectangles in three-D format. Information technology does not display the information on three axes.
-
100% stacked bar chart and 100% stacked bar nautical chart in 3-D Compares the percent that each value contributes to a full beyond categories. A 100% stacked bar in 3-D chart displays the horizontal rectangles in 3-D format. It does non display the data on three axes.
-
Horizontal cylinder, cone, and pyramid chart Available in the same amassed, stacked, and 100% stacked chart types that are provided for rectangular bar charts. They show and compare data the aforementioned way. The just divergence is that these chart types brandish cylinder, cone, and pyramid shapes instead of horizontal rectangles.

Data that is arranged in columns or rows on an Excel canvass can be plotted in an area nautical chart. By displaying the sum of the plotted values, an area chart also shows the human relationship of parts to a whole.
Surface area charts emphasize the magnitude of change over time, and can exist used to depict attention to the full value beyond a tendency. For instance, data that represents profit over time tin can exist plotted in an surface area nautical chart to emphasize the total profit.
Area charts have the post-obit chart subtypes:
-
Surface area nautical chart Displays the trend of values over time or other category data. 3-D area charts utilize three axes (horizontal, vertical, and depth) that you can change. More often than not, consider using a line chart instead of a nonstacked surface area chart because data from 1 series can be obscured past data from another series.
-
Stacked area chart Displays the tendency of the contribution of each value over time or other category information. A stacked surface area chart in 3-D is displayed in the same manner but uses a 3-D perspective. A iii-D perspective is not a true 3-D chart considering a tertiary value axis (depth centrality) is not used.
-
100% stacked area chart Displays the tendency of the percentage that each value contributes over time or other category data. A 100% stacked area nautical chart in 3-D is displayed in the aforementioned manner but uses a 3-D perspective. A 3-D perspective is non a true iii-D chart considering a third value axis (depth axis) is not used.

Data that is arranged in columns and rows on an Excel sheet tin be plotted in an xy (scatter) chart. A scatter nautical chart has two value axes. It shows one ready of numeric data along the horizontal axis (x-axis) and some other along the vertical axis (y-centrality). It combines these values into single information points and displays them in irregular intervals, or clusters.
Besprinkle charts evidence the relationships among the numeric values in several data series, or plot two groups of numbers as i series of xy coordinates. Scatter charts are typically used for displaying and comparing numeric values, such as scientific, statistical, and engineering information.
Scatter charts have the following chart subtypes:
-
Besprinkle chart with markers only Compares pairs of values. Use a scatter chart with data markers just without lines if you accept many information points and connecting lines would brand the information more difficult to read. You can also use this chart type when you do not have to show connectivity of the information points.
-
Besprinkle chart with smoothen lines and scatter nautical chart with smoothen lines and markers Displays a smoothen bend that connects the data points. Smooth lines can be displayed with or without markers. Apply a smooth line without markers if in that location are many data points.
-
Scatter chart with straight lines and scatter chart with directly lines and markers Displays directly connecting lines between data points. Straight lines can exist displayed with or without markers.

A bubble chart is a kind of xy (scatter) nautical chart, where the size of the bubble represents the value of a third variable.
Bubble charts accept the post-obit chart subtypes:
-
Bubble chart or bubble chart with 3-D consequence Compares sets of three values instead of ii. The 3rd value determines the size of the bubble mark. You can choose to brandish bubbles in ii-D format or with a 3-D outcome.

Information that is arranged in columns or rows in a specific order on an Excel canvass tin exist plotted in a stock nautical chart.
As its name implies, a stock chart is most frequently used to evidence the fluctuation of stock prices. Withal, this nautical chart may as well exist used for scientific data. For example, yous could use a stock chart to indicate the fluctuation of daily or annual temperatures.
Stock charts have the following nautical chart sub-types:
-
Loftier-depression-close stock nautical chart Illustrates stock prices. It requires three series of values in the correct order: loftier, depression, and and then shut.
-
Open-high-depression-close stock chart Requires iv series of values in the correct social club: open, high, depression, and so close.
-
Volume-loftier-depression-close stock chart Requires four series of values in the right order: volume, loftier, low, and then shut. Information technology measures volume by using two value axes: one for the columns that measure volume, and the other for the stock prices.
-
Volume-open-loftier-low-shut stock nautical chart Requires v series of values in the correct club: volume, open, high, low, and then shut.

Data that is arranged in columns or rows on an Excel sheet tin be plotted in a surface chart. Every bit in a topographic map, colors and patterns betoken areas that are in the aforementioned range of values.
A surface chart is useful when you want to find optimal combinations between two sets of information.
Surface charts accept the following nautical chart subtypes:
-
3-D surface chart Shows trends in values beyond two dimensions in a continuous curve. Color bands in a surface chart do not correspond the information series. They represent the difference between the values. This chart shows a three-D view of the data, which can be imagined as a prophylactic sheet stretched over a 3-D cavalcade nautical chart. It is typically used to show relationships between large amounts of data that may otherwise be difficult to see.
-
Wireframe iii-D surface chart Shows just the lines. A wireframe three-D surface chart is not piece of cake to read, but this nautical chart blazon is useful for faster plotting of big data sets.
-
Contour nautical chart Surface charts viewed from above, similar to two-D topographic maps. In a profile chart, color bands represent specific ranges of values. The lines in a profile nautical chart connect interpolated points of equal value.
-
Wireframe contour nautical chart Surface charts viewed from higher up. Without color bands on the surface, a wireframe chart shows only the lines. Wireframe contour charts are not easy to read. You lot may want to use a 3-D surface nautical chart instead.

Similar a pie chart, a doughnut chart shows the relationship of parts to a whole. However, it can contain more than than one information series. Each ring of the doughnut chart represents a data series.
Doughnut charts take the following chart subtypes:
-
Doughnut nautical chart Displays data in rings, where each ring represents a data serial. If percentages are displayed in data labels, each ring will total 100%.
-
Exploded doughnut chart Displays the contribution of each value to a total while emphasizing individual values. However, they can contain more than one data serial.

In a radar chart, each category has its own value axis radiating from the middle point. Lines connect all the values in the same series.
Use radar charts to compare the aggregate values of several data series.
Radar charts have the post-obit chart subtypes:
-
Radar chart Displays changes in values in relation to a center signal.
-
Filled radar nautical chart Displays changes in values in relation to a center point, and fills the area covered by a information series with color.
Modify a nautical chart blazon
If you lot have already have a chart, but yous just want to change its type:
-
Select the chart, click the Chart Pattern tab, and click Modify Chart Type.
-
Select a new chart blazon in the gallery of available options.
Run into Likewise
Create a nautical chart with recommended charts
Which Chart Type Displays The Data Horizontally,
Source: https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/office/available-chart-types-in-office-a6187218-807e-4103-9e0a-27cdb19afb90
Posted by: quinnupought.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Chart Type Displays The Data Horizontally"
Post a Comment